Simple Machines Levers Let's Talk Science

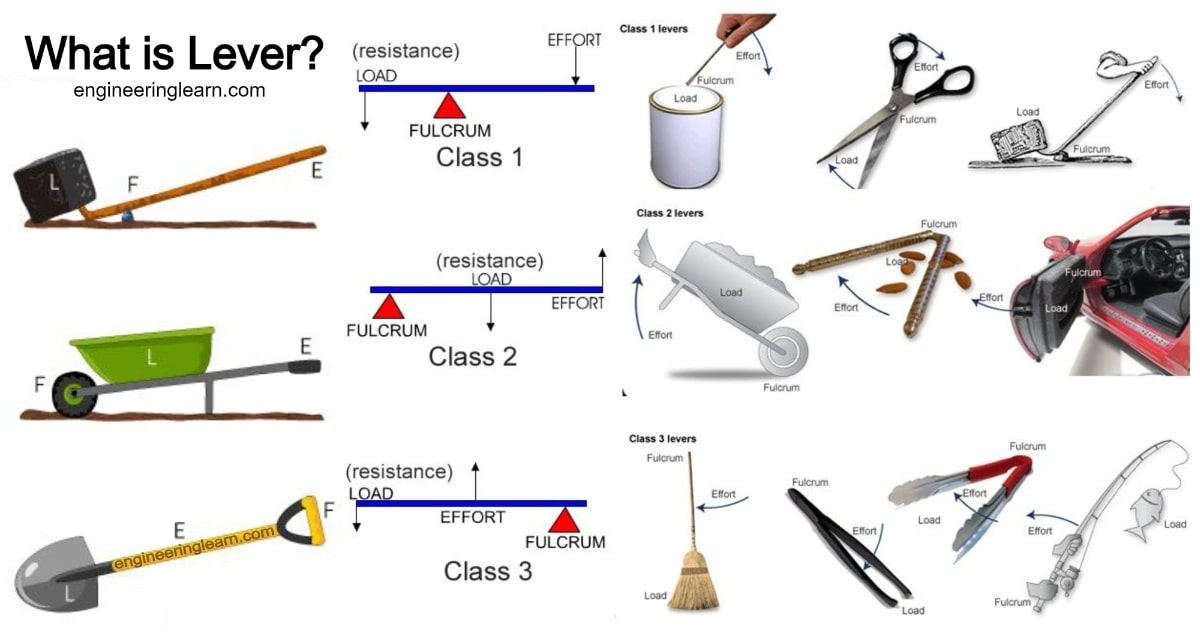
The 3 Classes of Levers
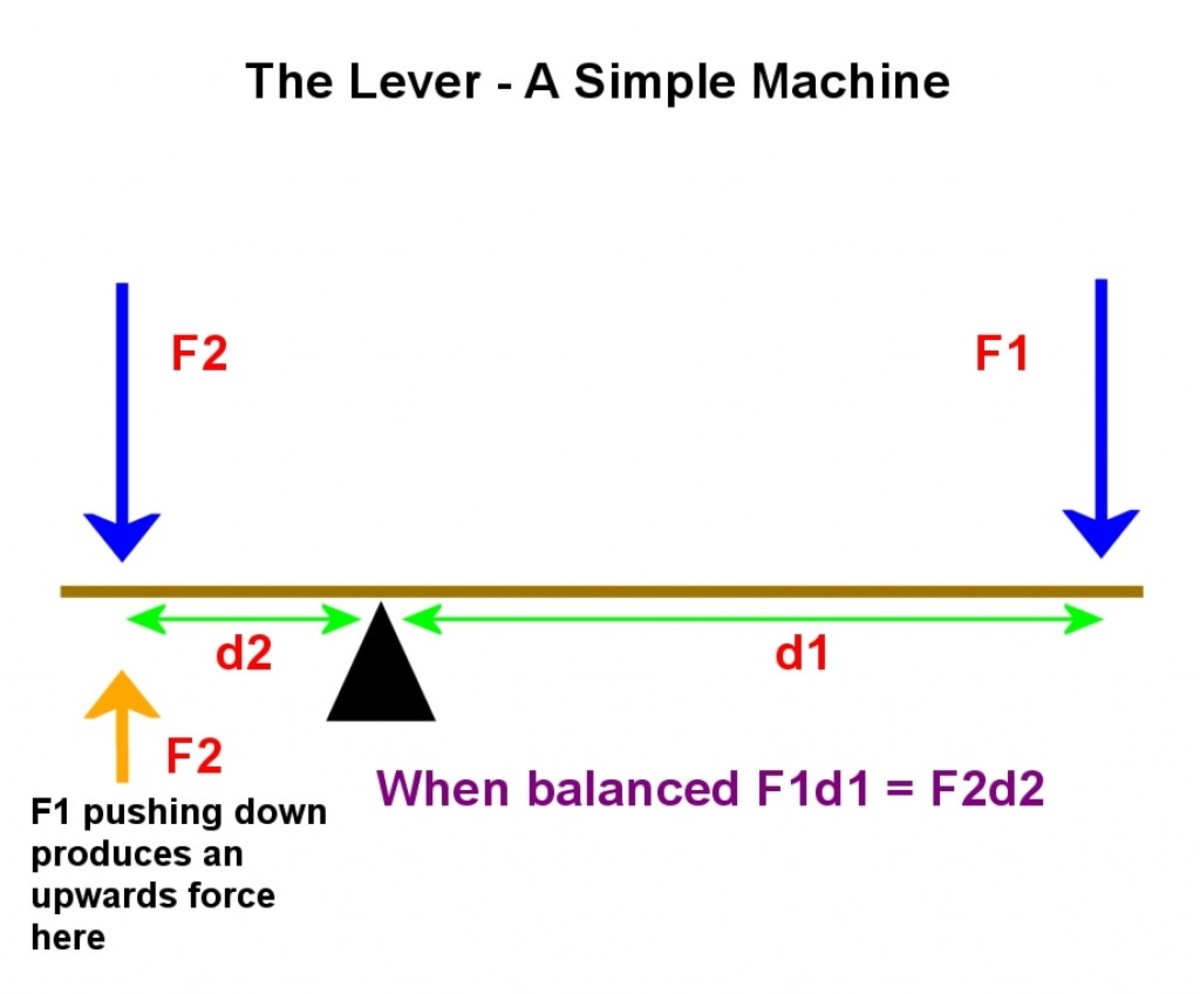
A lever is a simple machine made of a rigid beam and a fulcrum. The effort (input force) and load (output force) are applied to either end of the beam. The fulcrum is the point on which the beam pivots. When an effort is applied to one end of the lever, a load is applied at the other end of the lever. This will move a mass upward.

The 3 Classes of Levers
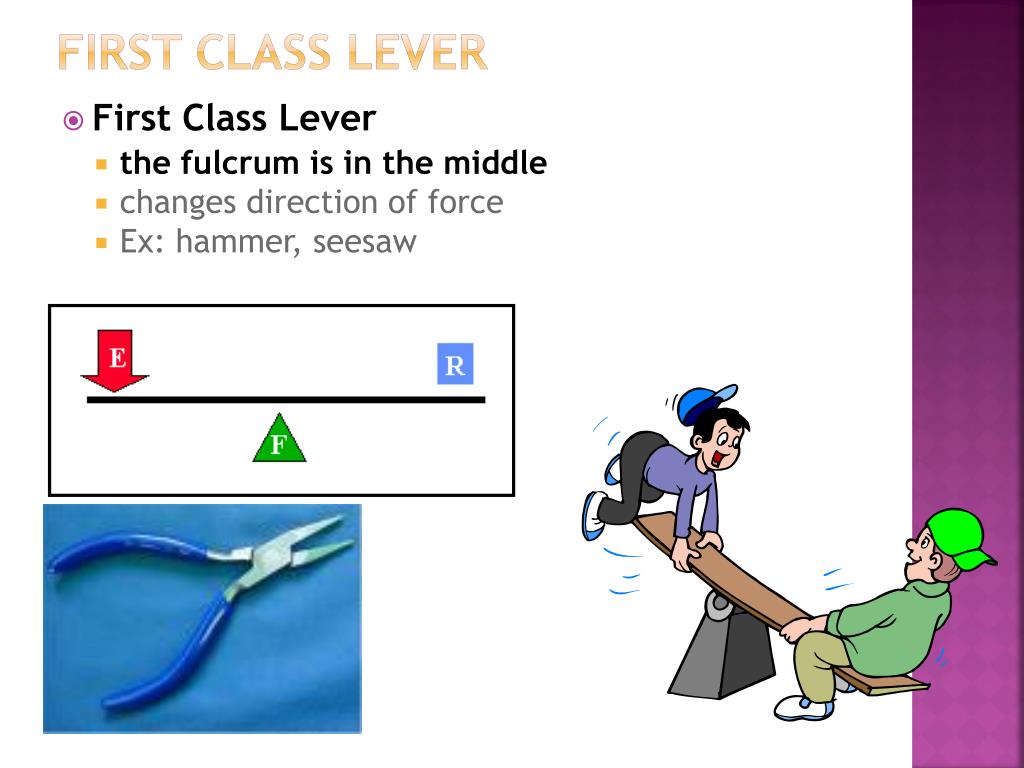
A first class lever is a lever where the fulcrum is located between the load and the effort. If the fulcrum is nearer to the load, then we can use less effort to move the load. However, if the fulcrum is located nearer to the effort, then we'll need to use more effort to move the load. If the fulcrum is located in the middle of the arm, we.

PPT LEVERS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2710686
a load or resistance that is placed on the rigid structure (weight of body part being moved and anything that it is carrying) A typical lever There are three types of lever. 1. First class.
Simple Machines How Does a Lever Work? Owlcation
A lever that has its fulcrum (point of support or axis of rotation) between the point of resistance (load) and the point of effort (applied force). In the human body, a first class lever is used when the head is raised off the chest. first class lever From: first class lever in The Oxford Dictionary of Sports Science & Medicine »

First Class Lever images
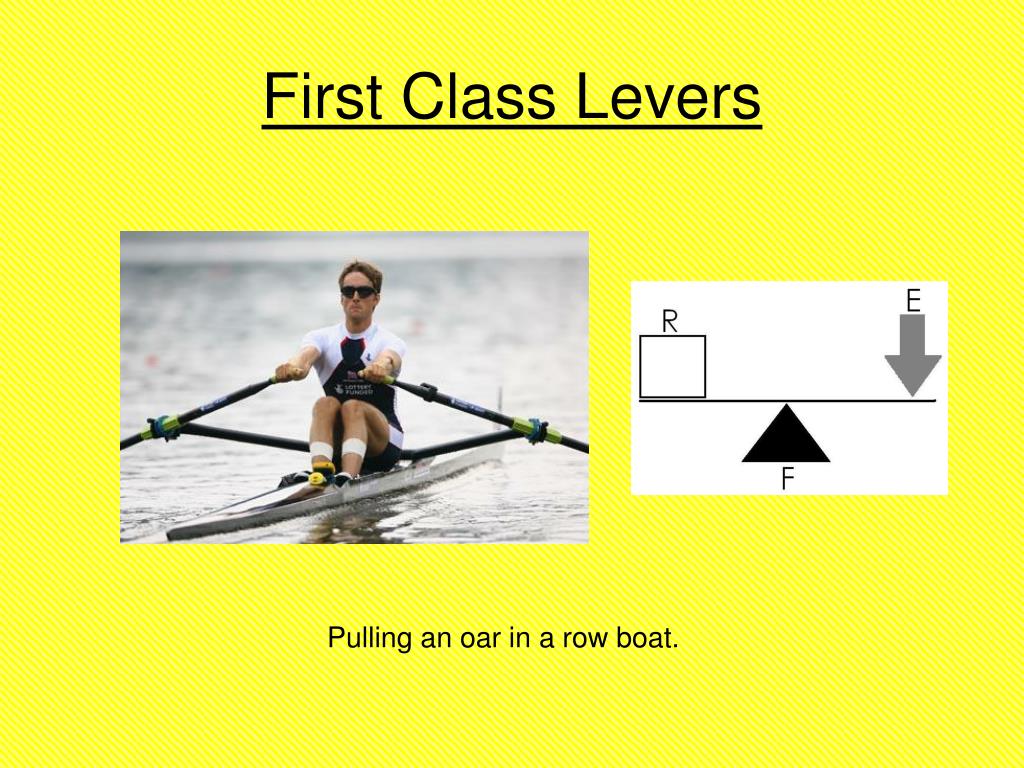
A seesaw is a first-class lever. First-class levers in the body are rare, and few exercises utilize them. Examples, however, are exercises that require elbow extension, such as dumbbell triceps extensions, cable triceps push-downs and triceps dips.
Explain the Difference Between 1st 2nd and 3rd Class Levers ItzelkruwDuncan
First Class Lever. Examples - Car jack, crowbar, seesaw, boat oar, scissors, pliers, claw hammer, bolt cutter, and wire stripper. 2. Second Class. Also known as Class 2 or 2nd class lever, the fulcrum is at one end of the beam, and the effort is at the other end. The load is located between the fulcrum and effort.
PPT Types of Levers PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1897391
First class Lever: The fulcrum of this type of lever is located between the weight and the force applied. The force-fulcrum-weight order is used to describe it. The most basic form of lever is this one.By looking at the options we can identify that crowbar and scissors are examples of first class levers.
PPT Biomechanics PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2573023
First Class Lever Examples. A first class lever is a type of lever where the fulcrum is located between the load and the effort. Examples of first class levers include a seesaw, the common scissors, a crowbar, a bottle opener, and a wheelbarrow. In each of these examples, the force applied (effort) is located on one side of the fulcrum, while.

First, second and third class lever system graphic OER Commons
What is the first class lever or class I lever? The lever which has a Fulcrum or pivot point in between the Load and Effort is called first class lever. Give examples of first class lever Seesaw is an example of first class lever where the pivot (fulcrum) is in the middle. seesaw - class I lever
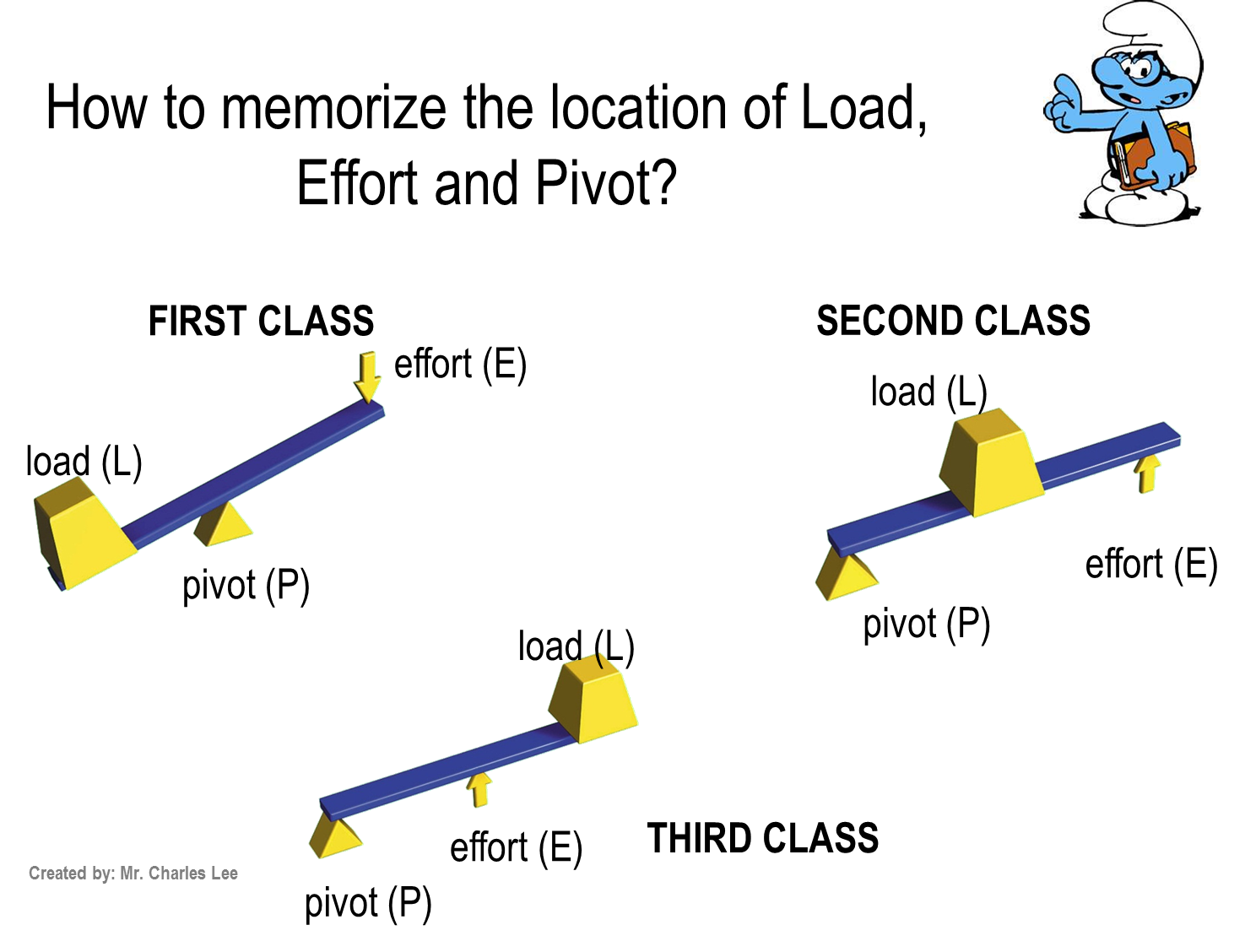
Levers How to distinguish the classes of lever
First-class levers. First-class levers are the simplest types of lever, where the two forces, the effort and the resistance, are applied on opposite sides of the fulcrum (Figures 4). In the body, the best example of a first-class lever is the way your head is raised off your chest (Figure 5).
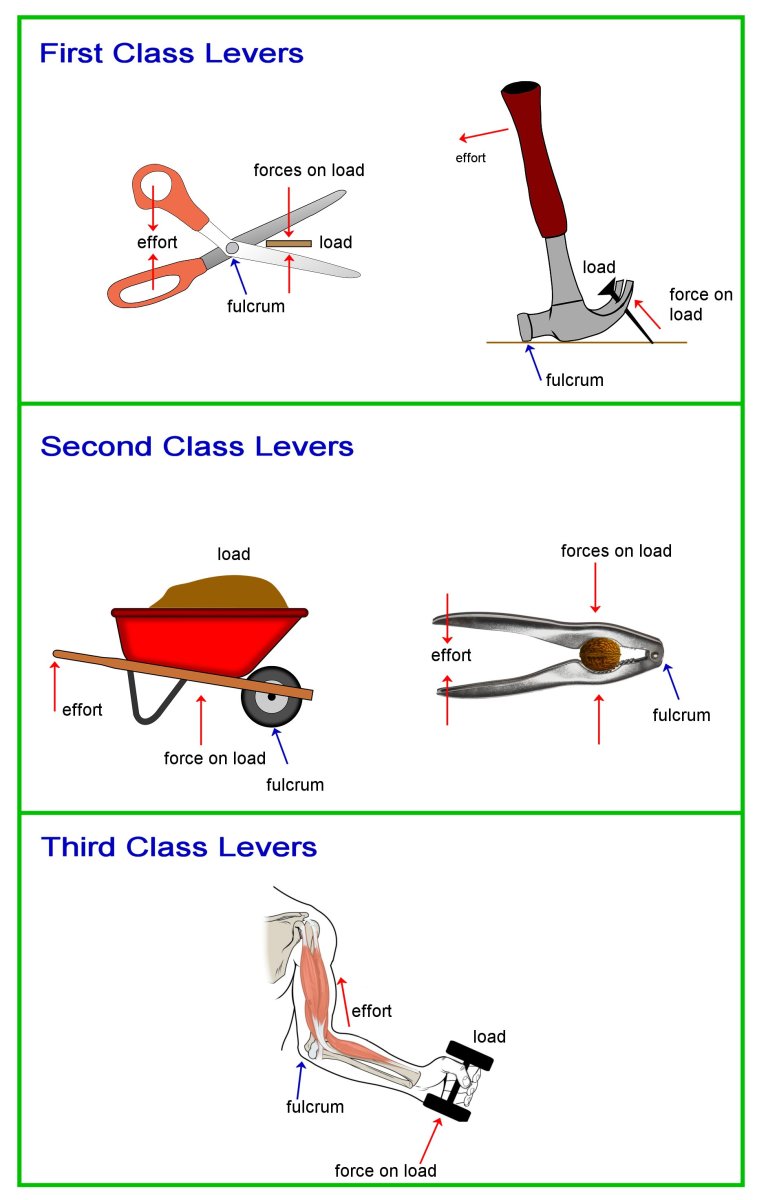
Simple Machines How Does a Lever Work? Owlcation
An example of a first class lever in the human body is the head and neck during neck extension. The fulcrum (atlanto-occipital joint) is in between the load (front of the skull) and the effort (neck extensor muscles). The muscles are attached to the posterior part of the skull to allow for the greatest effort arm. The atlanto-occipital joint in.

The 3 Classes of Levers
First Class Lever What is a first class lever? Here we look at first, second and third class levers, and the differences between them. We also look at how first class levers work in machinery and in the human body. Additionally, we suggest some great teaching resources all about the different classes of levers.

What is Lever? Principle, Types, And Examples
Anatomy of Levers, Part 1: First-Class Levers. A first-class lever is a very simple machine comprised of a beam placed upon a fulcrum. A load is placed onto one end of a beam, while an effort is directed onto the other end to counter the load. When viewing the illustrations, arrows indicate the direction of forces applied.
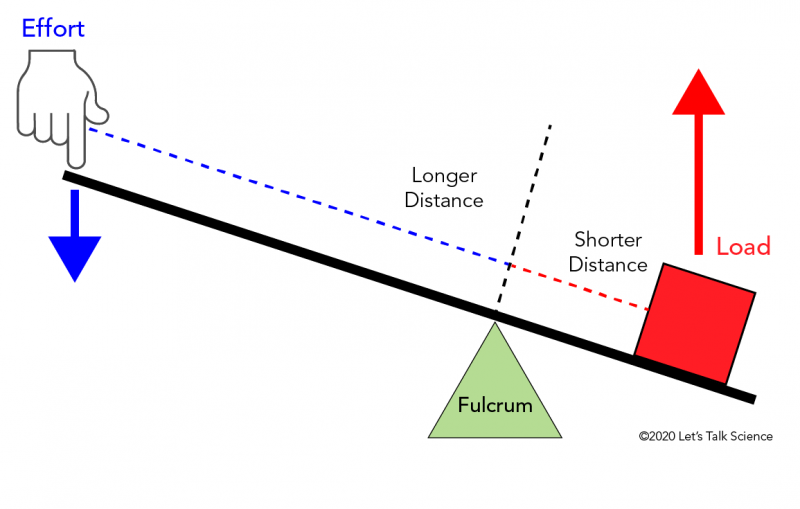
Simple Machines Levers Let's Talk Science
First-class Lever. In a first class lever, the load and force sit on either side of the pivot like a seesaw. First-class levers are relatively uncommon in the body, but one example is the triceps brachii muscle of the upper arm which acts to extend the forearm. The force is applied at its point of insertion on the ulna in the forearm, the elbow.
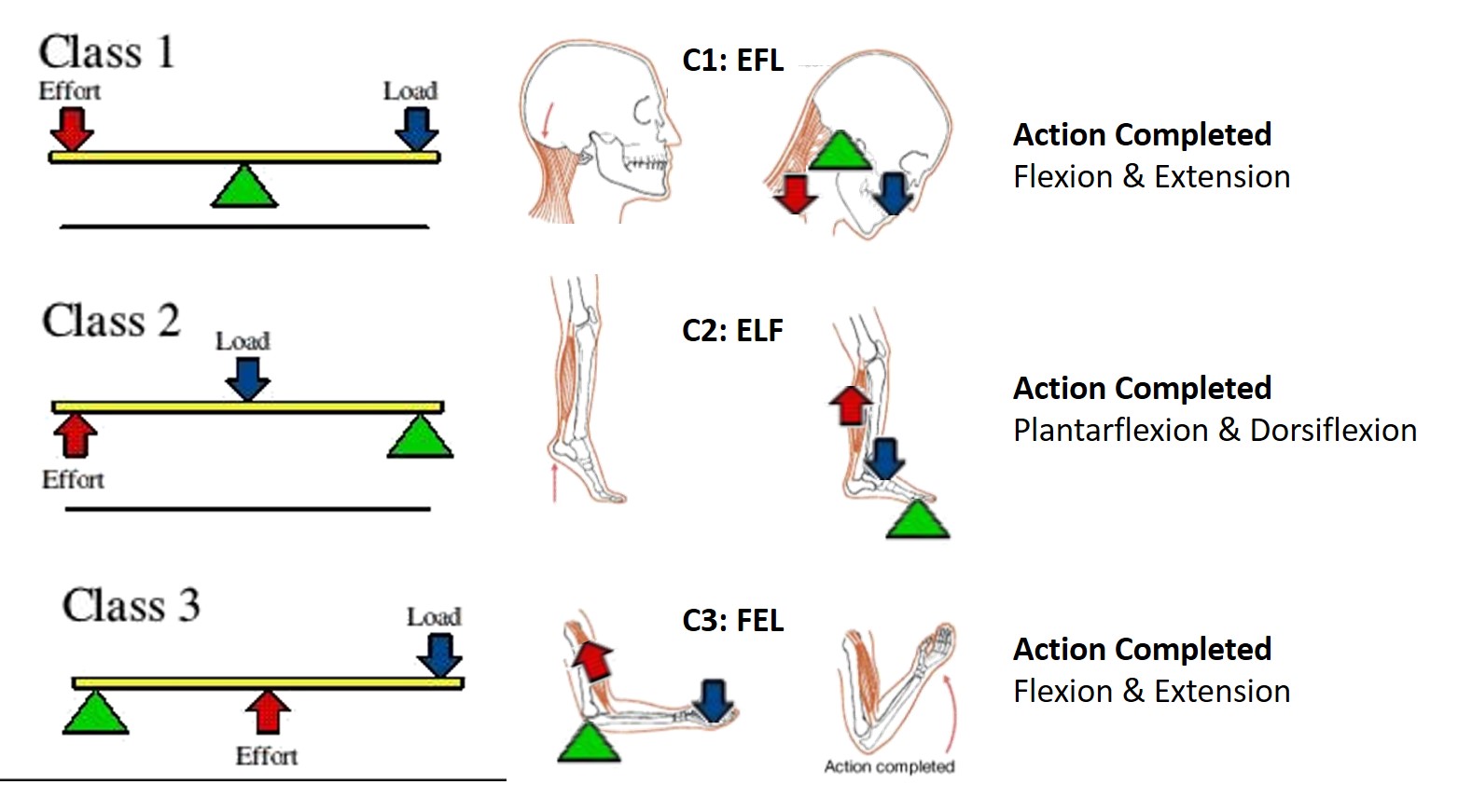
Understanding the three types of levers in the body
A first-class lever has the fulcrum in the middle and the load and effort on each side of the fulcrum. Its mechanical advantage is equal to 1. A seesaw is an example of a first-class lever because the fulcrum lies between the effort and the load.

PPT Levers in the Human Body PowerPoint Presentation ID419935
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or fulcrum. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is divided into three types. It is one of the six simple machines identified by Renaissance scientists.